Home Assistant on OMV Container in Raspberry-Pi
-
The information provided on this website is intended to provide
a basic understanding of certain technologies and is not intended to
be a comprehensive guide.
-
Therefore, it should not be relied upon as the sole source of
information and should not be used as a substitute for professional
advice or expert analysis.
-
Please exercise caution when visiting or downloading from websites
mentioned on this website and verify the safety of the website and
software.
-
Some websites and software may be flagged as malware by antivirus
programs.
-
The reader assumes all responsibility for their use of the
information contained on this website and any consequences that may
arise.
-
The author disclaims any liability for any damages or losses that may
result from the use of this website or the information contained
herein.
-
The author reserves the right to update or change the information
contained on this website at any time without prior notice.
-
Any attempts to perform penetration testing or ethical hacking on
systems or networks should be done with the explicit permission of the
system/network owner.
-
Unauthorized access is illegal and can result in serious legal
consequences.
-
It is important to fully understand the scope of the testing and to
only test within that scope. Testing outside the agreed upon scope is
considered unauthorized and may result in legal action.
-
Any findings or vulnerabilities discovered during testing should be
reported to the system/network owner immediately and kept confidential
until a fix can be implemented.
-
It is recommended to use a separate, dedicated testing environment
rather than testing on a live production system to minimize the risk
of accidentally causing damage or downtime.
-
It is important to take steps to protect your own identity and
prevent accidental data leaks or exposure of sensitive information
during testing.
-
It is also recommended to follow a standard code of ethics for
ethical hacking and penetration testing.
Reference:
-
https://www.home-assistant.io/installation/linux
-
https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/onboarding/
-
https://github.com/JurajNyiri/HomeAssistant-Tapo-Control?tab=readme-ov-file
-
https://www.hass-agent.io/2.0/getting-started/
-
https://hub.docker.com/_/eclipse-mosquitto
-
https://github.com/sukesh-ak/setup-mosquitto-with-docker
-
https://github.com/NemesisRE/kiosk-mode
-
https://github.com/KTibow/fullscreen-card
Home Assistant on OMV Container in Raspberry-Pi :
Installing Home Assistant on Docker using OMV Compose, along with
Portainer, Jellyfin, and MQTT. Here’s the breakdown:
Home Assistant on OMV
-
Created the Home Assistant compose file
-
Completed onboarding and set up integrations
-
Added Tapo Cameras and enabled HACS integration
Other Services on OMV
-
Installed Jellyfin and Portainer using Docker Compose
-
Set up MQTT and connected it to Home Assistant:
-
Created the compose file and config
-
SSH into the container to add users/passwords
-
Added MQTT integration on Home Assistant
Installing HASS.Agent on Windows, connected via API token, and added
Windows sensors to Home Assistant.
https://www.gouti1454.com/p/kali-linux-hands-on.html#OMV7OMV-extras
Step 01: Enabling Docker repo
OMV -> System -> omv-extras -> check the box, then
save.

|
| OMV |
Step 02: Installing OMV-compose & plugins
OMV -> System -> Plugins
Search for the plugins, then click install icon :
openmediavault-compose
openmediavault-scripts

|
|
search for openmediavault
|
Now access Docker Compose under the hamburger menu
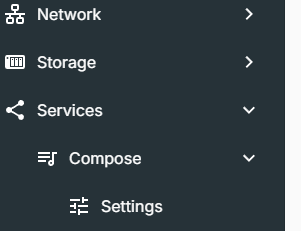
|
|
Docker compose menus appearing
|
Step 03: Creating Shared folder structure
Now Services -> Compose -> Settings
Next step is to add share folders for
Compose Files
Data
Backup
Now need to create share folders for the above
Click -> add then provide
Name
Filesystem
then save it

|
|
shared folder
|
Now going back to Services -> Compose -> Settings
To add the shared folders
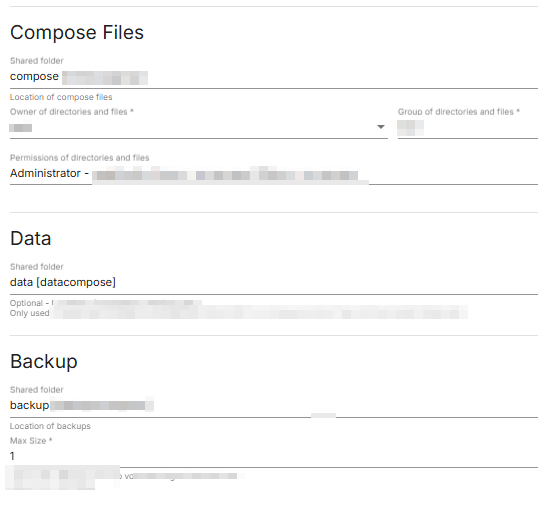
|
|
share folders added to compose settings
|
Step 04: Now Creating Docker Compose File to create containers.
Creating a User for Docker:
Give a name, then add the user to the groups and then check the box
for: disallow docker user account

|
|
Creating a User for Docker
|
Finding the uid & gid
pinas:~ $ id doceruser
uid=1001(doceruser) gid=100(users)
Home Assistant on OMV Container

|
|
HA:OMV dashboard
|
https://www.home-assistant.io/installation/linux
Step 01: homeassistant Compose file on OMV
OMV->Services->Compose->Files->add
----
services:
homeassistant:
image: ghcr.io/home-assistant/home-assistant:stable
container_name: homeassistant
network_mode: host
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
- TZ=Etc/UTC
- /run/dbus:/run/dbus:ro
volumes:
- /data/homeassistant/data:/config
- /run/dbus:/run/dbus:ro
ports:
- 8123:8123 #optional
restart: unless-stopped
-------
Once the container is up and running, following the onboarding
steps.
Step02: On-boarding
https://www.home-assistant.io/getting-started/onboarding/
Step03: Integrations
How to Add Tapo Cameras
https://github.com/JurajNyiri/HomeAssistant-Tapo-Control?tab=readme-ov-file

|
|
HA:CCTV dashboard
|
Step1:
Enabling Third party support in the Tapo app.
Me->Tapo lab->Third-party-compatibility
Step2
For each camera, need to enable camera username and password
Step 3:
Adding -> TP-Link integration in Home Assistance
Step 4:
For live streaming, use Onvif Integrations
Give IP address of the camera and port as 2020
Step 04: Hacs-integration
Installing hacs-integration

|
| Hacs-Integration |
https://hacs.xyz/docs/use/download/download/#to-download-hacs-container
pi@piraspi:~> sudo docker exec -i -t 1c4f56c6fe802 bash
wget -O - https://get.hacs.xyz | bash -
*******************
Jellyfin Compose file on OMV
services:
jellyfin:
image: jellyfin/jellyfin
container_name: jellyfin
network_mode: 'host'
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /data/config:/config
- /data/cache:/cache
-
/srv/dev-disk-by-uuid-765gvy/GNAS:/data/movies
- type: bind
source:
/srv/dev-disk-by-uuid-65765tvh/GNAS
target: /media
read_only: true
restart: 'unless-stopped'
extra_hosts:
- 'host.docker.internal:host-gateway'
**************
Portainer Compose file on OMV
services:
portainer:
image: portainer/portainer-ce:latest
container_name: portainer
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro
- /data/portainer/data:/data
ports:
- 9000:9000
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
**********************
MQTT docker container and connecting to Home assistant

|
| MQTT Integration |
Step 01: Compose file
services:
mqtt:
image: eclipse-mosquitto
container_name: mqtt
network_mode: 'host'
environment:
- PUID=1001
- PGID=100
- TZ=Etc/UTC
volumes:
- /data/mosquitto/config: /mosquitto/config
- /data/mosquitto/data: /mosquitto/data
- /data/mosquitto/log: /mosquitto/log
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- 1883:1883
- 9001:9001
***
Step 02: Docker pull command creating config file
pinas$:/data/mosquitto/config $ sudo nano mosquitto.conf
persistence true
persistence_location /mosquitto/data/
log_dest file /mosquitto/log/mosquitto.log
listener 1883
## Authentication ##
allow_anonymous true
Step 03: ssh into container and adding user/password
Portainer: Containers mqtt Console:/bin/sh

|
| Portainer:ssh |
#mosquitto_passwd -c /mosquitto/config/password.txt mqttuser1
Password:
retype Password:
Step 04: Adding user/password file path to config file.
pinas$:/data/mosquitto/config $ sudo nano mosquitto.conf
persistence true
persistence_location /mosquitto/data/
log_dest file /mosquitto/log/mosquitto.log
listener 1883
## Authentication ##
allow_anonymous false
password_file /mosquitto/config/password.txt
then, Restarting the container.
Step 05: Adding MQTT integration on HA
Input the server ip, Mqtt username and password which was
created.

|
| MQTT Integration |
Step 06: Installing Hass.Agent for Windows
https://www.hass-agent.io/2.0/getting-started/

|
|
Hass.Agent for Windows
|
Step 07: Getting API token from Home Assistant
Click profile name -> /profile/security -> scroll bottom click
"Long-lived access tokens"

|
|
API token from Home Assistant
|

|
|
Final Hass Agent for windows
|
Step 08: Adding Hass.Agent integration on HomeAssistant

|
|
Device Discovered on HA
|
Step 09: Adding Sensors on HASS.Agent on windows to reflect on HA

|
|
Adding Sensors
|

|
|
MTTQ HA Dashboard
|
***************************
KIOSK-Mode
HACS integration Kiosk-mode
Dashboard -> Edit -> Hamburger menu -> Raw Configuration
Editor
Add following code:
1. To hide header tabs for non admin user
2. To hide sidebar for particular user
kiosk_mode:
non_admin_settings:
hide_header: true
ignore_entity_settings: true
user_settings:
- users:
- home
hide_sidebar: true
kiosk: true
ignore_entity_settings: true
***************************
Home Assistant Calendar Integrations:
SunRise and SunSet Calendar:
Step-01: Using the below weblink one can create Google Sunrise and
Sunset calendar.
-
https://gearside.com/google-daylight-calendar/
-
https://www.php.net/manual/en/timezones.europe.php
Just update the Latitude, Longitude and TimeZone to reflect
correctly.
-
https://gearside.com/calendars/daylight.php?lat=52.950001&lng=-1.150000&timezone=Europe/London
Step-02: Go to google calendar -> Settings -> Add Calendar
-> add the URL
 |
| add the URL |
Enabling Google Calendar API:
Step-03: https://www.home-assistant.io/integrations/google/
 |
| enabling API |
Next Step-04 click "Create Credential" -> QAuth Client
ID
Select -> Application Type as -> "TVs and Limited input
devices"
 |
| Type as -> "TVs and Limited input devices |
 |
| Client ID and Client secret |
Next Step-05 Adding Google calendar integration on Home
Assistant:
Provide a friendly name and OAuth ID and Client ID, then open the
browser with the link provided and enter the code.
|
|
Refreshing calendar
|
More reference on
https://youtu.be/r2WbpxKDOD4?si=C0dOt3XBVnXw4ESZ
Step-06: Creating New calendar on Google Account
 |
| Creating New calendar |
 |
| Naming New calendar |
Step-07: Adding Trash Card Reminder card:
https://github.com/idaho/hassio-trash-card
 |
| Trash Card Reminder card |
Configuring the Trash Card to custom date format
 |
| custom date format |
Updating the detection pattern - keyword to pull the right calendar
invite.
 |
| detection pattern |
Final Calendar Dashboard

|
|
Calendar Dashboards
|
***************************
OpenHardWareMonitor Integration
https://www.home-assistant.io/integrations/openhardwaremonitor/
Step 01: OpenHardWareMonitor is running on windows machine,
Options-> Remote web server -> Run
Step02: Now need to edit configuration.yaml file of the HomeAssistant
Currently HomeAssistant is running in docker
To edit file inside the docker, get the volume addressed mapped on
docker.
 |
| To edit file inside the docker |
Adding Senor code to the configuration file
pi@pi:~ $ sudo nano /data/homeassistant/data/configuration.yaml
# Loads default set of integrations. Do not remove.
default_config:
# Load frontend themes from the themes folder
frontend:
themes: !include_dir_merge_named themes
automation: !include automations.yaml
script: !include scripts.yaml
scene: !include scenes.yaml
sensor:
- platform: openhardwaremonitor
host: 192.168.1.10
port: 8085
Step03: Restarting the HomeAssistant
Now all the Sensors of OpenHardwareMonitor are available under
Entities
 |
| OpenHardwareMonitor Entities |
********************
Configuring Telegram integrations:
https://www.home-assistant.io/integrations/telegram
Step01: Creating a Bot on your account
Follow the instructions listed below
-
https://core.telegram.org/bots#how-do-i-create-a-bot
Use the Bot to create an bot & get the API Key
Step02: Use the Bot account to get user id
Step03: Update the configuration.yaml file
pi@pi:~ $ sudo cat /data/homeassistant/data/configuration.yaml
# Telegram Bot
telegram_bot:
- platform: polling
api_key:
111111111111:aqswdfd5iunrve111iurnl67hdb-no111tihjronslkbnlk
allowed_chat_ids:
- 1234556789
- 00091234556789
# Notifier
notify:
- platform: telegram
name: Chat-ID-1
chat_id: 1234556789
- platform: telegram
name: Chat-id-02
chat_id: 00091234556789
Adding Blueprint template- Calendar Notifications & Actions
https://community.home-assistant.io/t/calendar-notifications-actions/612326
This Blue Print allows to set up Calendar Notification along with the Event Title and Event description to be passed-on.
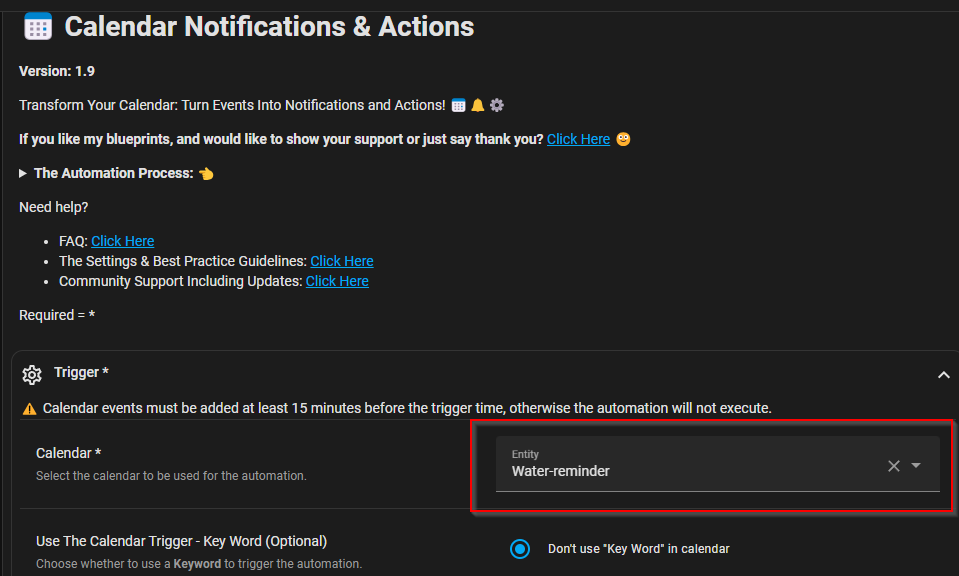 |
| Blue Print setup |
 |
| adding telegram trigger |
 |
| Telegram output |
*************************************
Tracking Linux System info using glances
Step 01; Installing
linux@inux:~$ sudo snap install glances
linux@linux:~$ sudo glances -V
Glances API version: 4
PsUtil version: 7.0.0
Log file: /tmp/glances-root.
ref: https://github.com/nicolargo/glances
Step 02: Running on BackGround:
Now to run the glances service on the background and starting using systemd
- Creating a file glances.service at /etc/systemd/system/
linux@linux:~$ sudo cat /etc/systemd/system/glances.service
[Unit]
Description = Glances in Web Server Mode
After = network.target
[Service]
User = glances
ExecStart = /opt/glances/venv/bin/glances -w -t 1
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.target
- Next enabling in systemctl
linux@linux:~$ sudo systemctl enable glances --now
linux@linux:~$ sudo systemctl start glances.service
linux@linux:~$ sudo systemctl status glances.service
linux@linux:~$ sudo reboot
- Checking the browser on :
https://localhost:61208
Step 03: Adding Glances to Home Assistant
Integration -> Glances
ref:
- https://github.com/nicolargo/glances/wiki/Start-Glances-through-Systemd
- https://github.com/nicolargo/glances/issues/2673
- https://www.home-assistant.io/integrations/glances/
**************************************











Comments
Post a Comment